Ok, so tomorrow is apparently not a regular Friday, but a good one. I would say, that is a very honest thing to call it, because what else would you call a Friday that is a day off? Sure, it's good. So that's what we are doing on that day - being closed and away, […]

Robot Costume Hack

Since Halloween is just around the corner we've built and published a few projects in order to give some ideas to the DIY costume-inclined folks. One is DIY Halloween RGB LED Kitty Ears and two is Halloween LED Witch Hat.
So for this third hack we started with an online-bought robot costume, but being a creative tech people, we couldn't resist making it better by using some brilliant LED strips that react to sound.
Supplies used:
- 3 x 5V RGB LED Stripxels WS2812B (30 per meter)
- 1 x 5V RGB Addressable LED strip, 1M (144 per meter)
- 1 x MEMS Microphone Board
- 1 x PJRC Teensy USB Board, Version 3.2
- 5 x Losi Micro-T MX2.0 2-pin connector set, wired
- 2 x Lithium Polymer Battery - 2000mAh (Lipo)
The Teensy was chosen because it has hardware based Fast-Fourier-Transform optimizations, and lots of memory.
The dense LEDs (144 per meter) were used on the helmet. More spaced apart (30 per meter) were used on the arms. All of them drive from one Teensy receiving analog signal from the microphone located in the helmet. The microphone captures both the voice of the wearer and ambient sounds.
Here's what it looks like reacting to the music:
Technical Build:
The idea was to attach two denser LED strips to the face mask guard and the rest to the arms of the costume. They both would react to ambient sound and light up depending on the frequency of sound. The helmet's strip would have the lower frequencies in the middle and the arms would have them start at the wrists.
The face mask guard took 52 LEDs per strip and arms got 25 LEDs per arm. These calculations are reflected in the code below.
For the arms, I divided each LED strip into two sections (since the costume itself had separate foam pieces for forearm and shoulder), and gave them their own battery. That allowed me to have a simple 2 pin connection for joining the arms to the helmet.
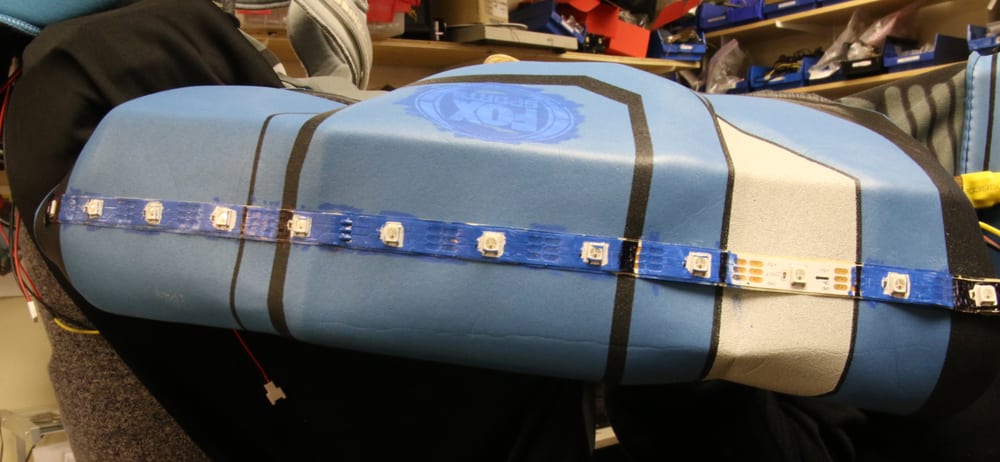

One problem when dealing with RGB Strips on wearables is that the solder pads are small and the wires break off too easily. I tried to minimize this by adhering a small wooden backing to the end of each strip. This acts like a cast and, when sealed with heat shrink, immobilizes the connections. I cut the supports on the laser cutter, but you can use anything. Popsicle sticks would work as well.

Here is the basic wiring diagram I used:
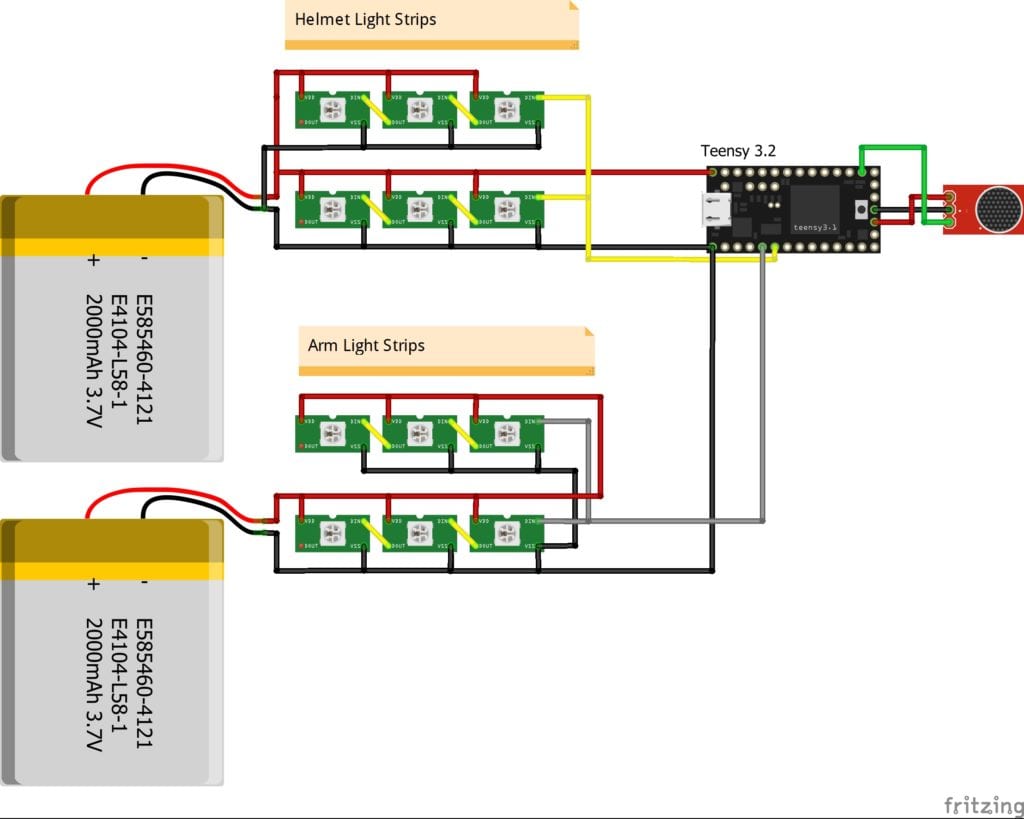
Software:
This code uses hardware support for FFT that's built into the Teensy. If you want to use a different processor, you will need to add a FFT library and modify the code accordingly.
I found some code online that was almost perfect for this project. Rather than reinventing the wheel, I reused that code, and modified it for my needs. Original credit has been left in the code.
Summary:
With Halloween just around the corner, this costume should be a hit at any event.. I can't wait to wear it!
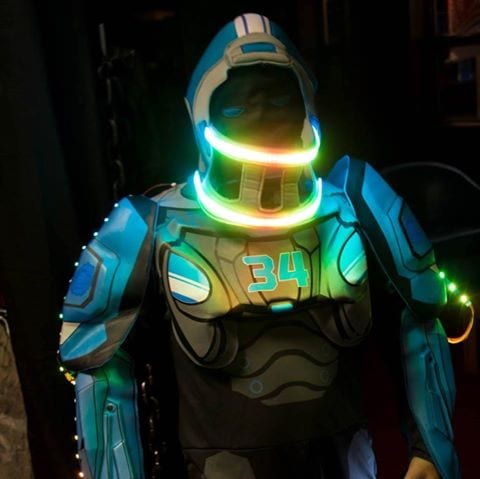

photo credit Lucky Shot (David Luckman)
MORE POSTS
If you were trying to visit us here Friday/Saturday, you would notice that we were "404" (site down). Sorry about that. Our host ISP is going through some changes that are ...aren't... going as well as they'd like. Sorry about the problems. Shouldn't be nothing that we can't get fixed, as soon as I find […]
Wow! They're finally here! These are the original gear motors we used sooo many years ago to convert and power the Miniball kits (yes, they're under review for bringing back - don't rush us!). We're the only place to find the whole assortment of four gear ratios - 75.7, 134.5, 196.6, and 297.1:1 reduction, and […]
We've got confirmation from the Santa Fe Art Institute that they are indeed handling the registration. Contact Brandy at (505) 424 5050 for registration details, or email her at info@sfai.org. Remember, this will most likely be the last hurrah for the event on May 3-6, 2001, so come now, or never again! Read More...
Solarbotics, Ltd. is not responsible for misprints or errors on product prices or information. For more information, please see our Terms and Conditions.
Warning: This product contains chemicals known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm.
Please visit www.P65Warnings.ca.gov for more information. This item was manufactured prior to August 31, 2018.

