A handy tutorial explaining how to put together the RGB LED Horns. Make your own, or get a kit with everything included (except for the paint). Supplies: Fosshape 300 2 x slow scroll RGB LED 2 x coin cell batteries conductive thread 2 x coin cell battery holder - sewable 2 x pieces of velcro […]
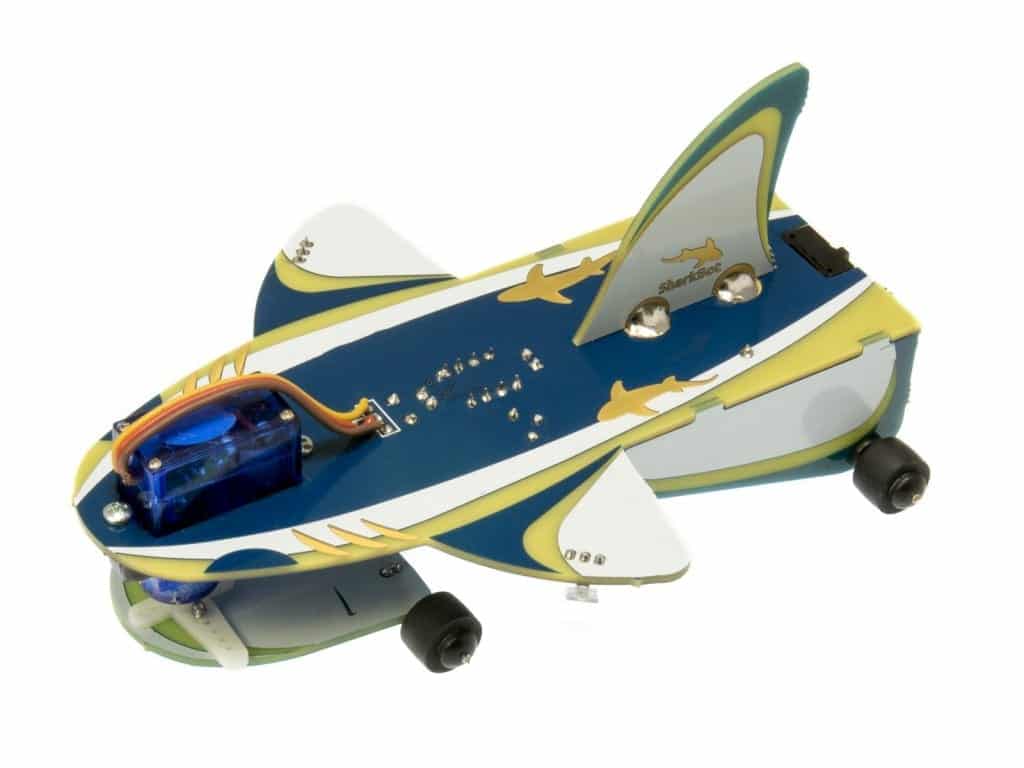

Project Monday: The Story of SharkBot
Not every product we design is destined to make it to the consumer. Sometimes a great idea gets taken to completion before we realize that one factor or another dooms it to an existence in our failed project bin.  One such project that now lives a watery grave is the Sharkbot. Akin to our much loved Herbie the Mousebot, the Sharkbot was a light seeking, semi-intelligent robot with a unique and quirky movement mechanic. Instead of driving along with a regular DC motor, the Sharkbot used a servo motor to “wiggle” the front wheel set back and forth, propelling it forward, not unlike a shark or fish would wiggle their tail to do the same. But up front, using... wheels. Trust us, it's cool.
One such project that now lives a watery grave is the Sharkbot. Akin to our much loved Herbie the Mousebot, the Sharkbot was a light seeking, semi-intelligent robot with a unique and quirky movement mechanic. Instead of driving along with a regular DC motor, the Sharkbot used a servo motor to “wiggle” the front wheel set back and forth, propelling it forward, not unlike a shark or fish would wiggle their tail to do the same. But up front, using... wheels. Trust us, it's cool.
Watch video:  We fell in love with the idea way back in 2007 after buying a wiggle/swing car (a.k.a. "Plasma car") for the kids, but ended up having the staff run laps around the office on it instead. What a cool idea... We prototyped a robot chassis using a simple DC gearmotor driven by a BEAM light-responsive "Bicore" oscillator. With one motor we were able to get propulsion, direction, and even reversing with minimal mechanics and electronics. Plus, it looked fabulous. We had to try to make this into a seriously fun robot.
We fell in love with the idea way back in 2007 after buying a wiggle/swing car (a.k.a. "Plasma car") for the kids, but ended up having the staff run laps around the office on it instead. What a cool idea... We prototyped a robot chassis using a simple DC gearmotor driven by a BEAM light-responsive "Bicore" oscillator. With one motor we were able to get propulsion, direction, and even reversing with minimal mechanics and electronics. Plus, it looked fabulous. We had to try to make this into a seriously fun robot.
 After several prototypes, we got to a stage where it needed some love to get past the 80% mark. Unfortunately, other projects took priority, and it languished until just earlier this year. We updated the mechanics to use a servo and microcontroller, sourced better light sensors, and gave it a truly sleek PCB design that pushed the abilities of our PCB house (they wanted to keep one as a showpiece). However, this is when the Sharkbot became beached.
After several prototypes, we got to a stage where it needed some love to get past the 80% mark. Unfortunately, other projects took priority, and it languished until just earlier this year. We updated the mechanics to use a servo and microcontroller, sourced better light sensors, and gave it a truly sleek PCB design that pushed the abilities of our PCB house (they wanted to keep one as a showpiece). However, this is when the Sharkbot became beached.
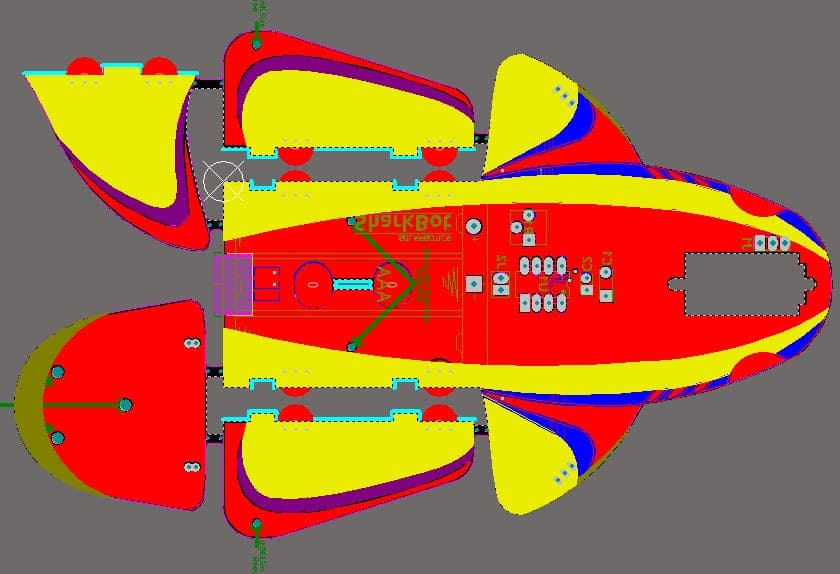 While new PCB design companies have been bringing down the cost of PCB fabrication, the raw cost of FR4, the main ingredient in a printed circuit boards, is still considerable. With the Sharkbot using a 7 x 4.5" PCB, it wasn't cost effective for what the kit did. Replacing some of the body materials with less-expensive alternatives brought up new fabrication challenges. Mechanical constraints of battery and servo sizes make it near impossible to reduce the size. As beautiful as it is, it just didn't offer enough value in what it did to justify the price.
While new PCB design companies have been bringing down the cost of PCB fabrication, the raw cost of FR4, the main ingredient in a printed circuit boards, is still considerable. With the Sharkbot using a 7 x 4.5" PCB, it wasn't cost effective for what the kit did. Replacing some of the body materials with less-expensive alternatives brought up new fabrication challenges. Mechanical constraints of battery and servo sizes make it near impossible to reduce the size. As beautiful as it is, it just didn't offer enough value in what it did to justify the price.
In other words, it lacked bang for the buck.
 The project isn't a total loss, as we did learn some wicked cool PCB fabrication techniques we're bringing into other designs, and we learned how to identify shortcomings in a project much earlier in the design phase. Unfortunately, until we can come up with a less expensive to build Sharkbot, it's going to remain a shelfbot.
The project isn't a total loss, as we did learn some wicked cool PCB fabrication techniques we're bringing into other designs, and we learned how to identify shortcomings in a project much earlier in the design phase. Unfortunately, until we can come up with a less expensive to build Sharkbot, it's going to remain a shelfbot.
MORE POSTS
We're involved with a couple of upcoming workshops featuring our Sumovore Mini-Sumo! (No local link yet, until it's officially on sale - sorry!) The first one is at the Northern Alberta Institute of Technology (NAIT) Open House in Edmonton, Alberta. Besides a mini-sumo, full-size sumo, fire-fighting, and line-follower, they're also running two workshops, one on […]
Got another update from Chance "knitsu" Brown that he's got some high-resolution images and videos of his Roboraptor online now. After some initial browsing, didja know that there's going to be two books on the Robosapien soon? And there's several online communities? (Here's one)
The Western Canadian Robot Games are close at hand (umm... this weekend!), and in response to popular request, we're cranking up the SolarSpeeder contest again! Ever built a Solarbotics SolarSpeeder? Bring it down to the games, enter at our booth (free!), and we'll run a SolarSpeeder target race. Aim your racer at a 10cm (4") […]
Solarbotics, Ltd. is not responsible for misprints or errors on product prices or information. For more information, please see our Terms and Conditions.
Warning: This product contains chemicals known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm.
Please visit www.P65Warnings.ca.gov for more information. This item was manufactured prior to August 31, 2018.

